If licensed at your site, N4 automatically checks for overstowed real or projected containers, also called overstow. A container is considered overstowed if it is positioned above a container that is destined for a preceding port and therefore requires rehandling. Like other stowage errors, overstow errors appear in the Stowage Warnings window.
The XPS client graphically identifies overstowed containers with a circle inside small and large container icons, as shown in the following figure.

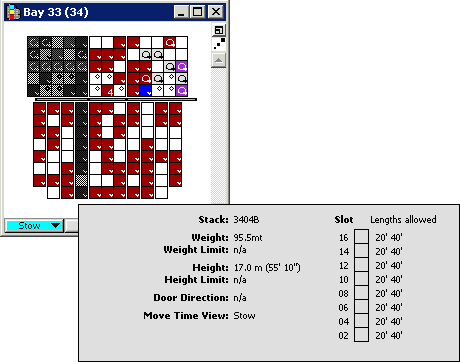
You can view overstow dependencies in scan views. Overstow dependencies for below-deck stacks are the container slots in the stack (and all the above-deck stacks, as necessary) that must be cleared to enable access. Viewing overstow dependencies requires the following:
The ship must be defined in ShipEditor 1.3.3 or later. For more information, see the manual Using ShipEditor.
The vessel service must have the correct port rotation, as defined in the N4 client: N4 client  Configuration
Configuration  Carriers
Carriers  Carrier Services
Carrier Services  Carrier Services view
Carrier Services view  Carrier Services form.
Carrier Services form.
In the XPS client, you can view the port rotation in the Vessel Services dialog box.
When you edit the port of rotation of a vessel visit in N4 to a different rotation than the one defined in the corresponding service, N4 updates XPS. XPS automatically displays the deviant service in the Vessel Services dialog and also considers the deviant service in the overstow logic. XPS displays the deviant service visit only when the visit phase changes fromCreated to Inbound. XPS displays the non-standard port rotation only in the Vessel Services dialog.
To view overstow dependencies:
On the toolbar, select the information tool  .
.
In a vessel scan view, click below a stack.
The XPS client colors the stacks gray that must be cleared for proper access, and displays a stack information dialog, as shown in the following figure.